Manual for Coordinators
Daftar isi
- 1 Use of the website for administration and coordination
- 2 Â
- 3 Reports
- 4 Manage
- 5 Administration
- 6 Roles and responsibilities
Use of the website for administration and coordination
Registering new users and updating current users
All users of iSIKHNAS must be registered before they are able to use the system. This is the case for both data reporters and data viewers.
New users can be registered to the system in two ways
- in the field by an authorised person using their mobile telephone, or
- by an authorised person, usually the district iSIKHNAS coordinator, via the iSIKHNAS website.
Registration using the iSIKHNAS website
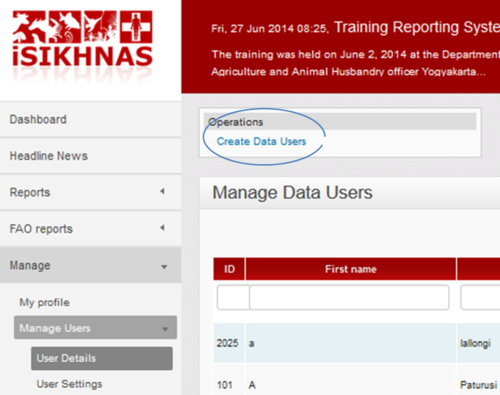
Using the iSIKHNAS main menu, go to Manage : Manage Users : User details.
Then click on Create Data User
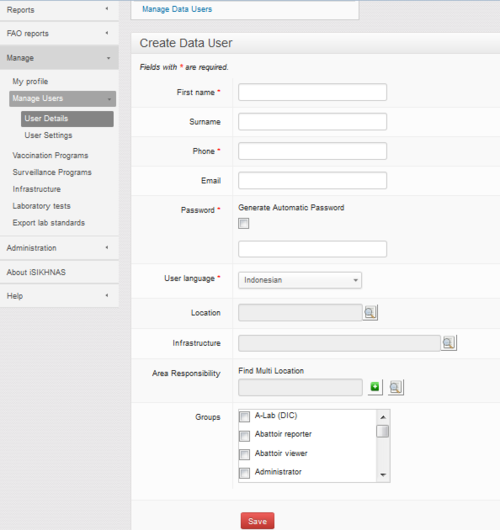
You will be taken to a new Create Data User form.
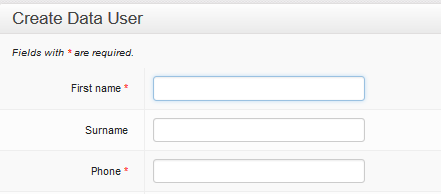
Click your mouse in the First name field. The outline colour will change to blue to show that it is active.
First name
Enter the first name of the new user. Try to use correct capitalisation for these name fields. Remember the user name will appear in multiple reports and other areas of the website. Please make sure it is correctly spelled and as complete as possible.
Surname
Move to the Surname field by either pressing  or by using your mouse to take you to the new field and clicking in the empty box. This field is only required for those people who use family names. Leave the field empty if there is no surname.
or by using your mouse to take you to the new field and clicking in the empty box. This field is only required for those people who use family names. Leave the field empty if there is no surname.
Phone
Next, enter the mobile phone number of the new user. This telephone number must be to the unique to the user. It must be the number to phone they use every day for their work. This telephone number will identify the new user to the system every time they report or query data.
Enter an email address if the person uses email. The address should be unique to the new user. It cannot be a group email address, or one that is used by other iSIKHNAS users. By adding an email address, a new user can arrange to have regular reports using iSIKHNAS data, sent by email. The email address can always be added or changed later.
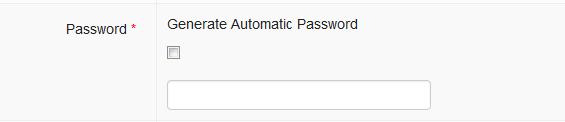
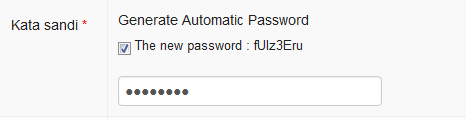
Password
The web password will be useful if users want to visit the iSIKHNAS website to
- Look up data on the site.
- Change a password.
- Change some user details.
You can click the checkbox Generate Automatic Password to ask the system to make a unique password for the new user. Write the password on a piece of paper and give it to the new user.
Passwords can be changed later by the user. Coordinators can also change passwords for users who have forgotten their password. You can either use a password chosen by the new user by writing the password into the empty field.
A word about passwords: Passwords should not contain personal information, whole words or well known characters or names. The best password are longer than 8 characters and created by coming up with an entire phrase that’s easy for the user to remember. Use the first letter, number or symbol from each word in the phrase, keeping punctuation intact as well. So, let’s take this, for example: Hi! I’m Dhony. I’m from Sulawesi and I like the number 3! Grab the first of each piece, and the password could become: H!ImDImfSul&Iltn3! That’s a good, strong, long password that’ll be hard to crack and easy to remember.
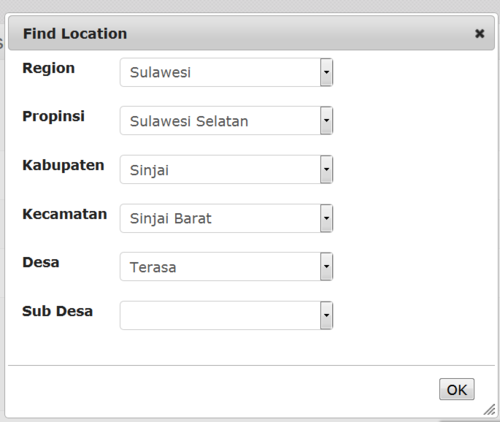
Location
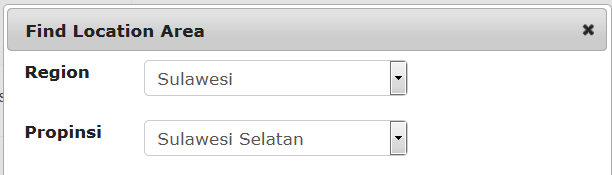
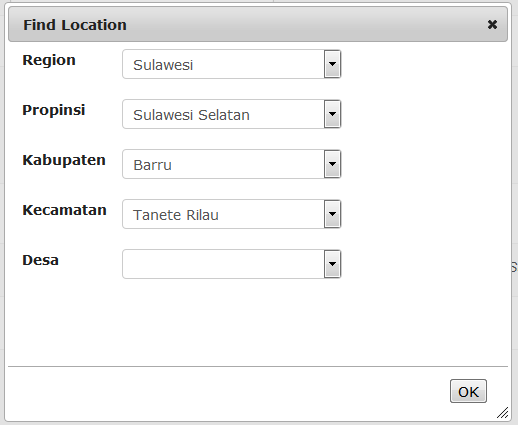
Choose the location of the usual place of work of the new user to the village (desa) level. Go through each level to pick from the drop down lists.
When you have finished click OK.
The full location code and name will appear on the form.
Infrastructure
New users can be assigned to infrastructure where they work. The main infrastructure types are
- Abattoirs
- Aggregation points
- Laboratories
- Semen collection points
- Markets
- Veterinary services offices
- Checkpoints
New infrastructure can be created by coordinators using the Manage : Infrastructure
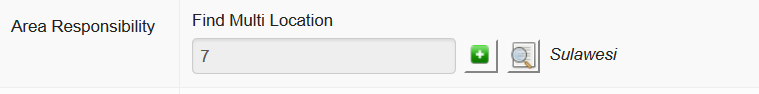
Area responsibility
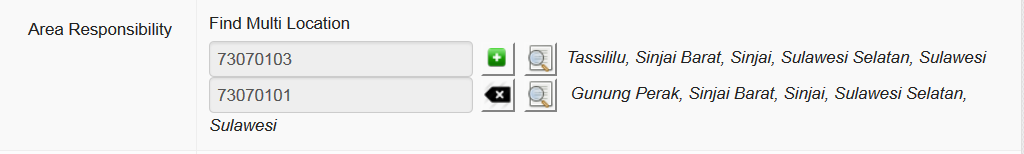
As well as being assigned to a particular working location - where a user is phyically based most of the time - users are assigned to one or more areas of responsibility. This defines the whole area the user works or is responsible for. This will tell iSIKHNAS that this person should receive alerts or information relevant to that area. It helps to filter the data for the user, to make sure only the most relevant data or alerts are sent.
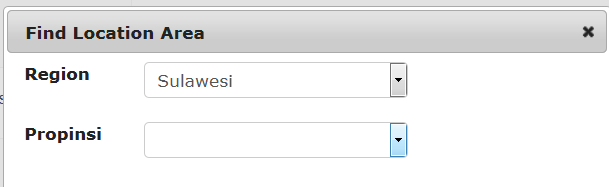
A regional coordinator for Sulawesi, for example, would be assigned as follows
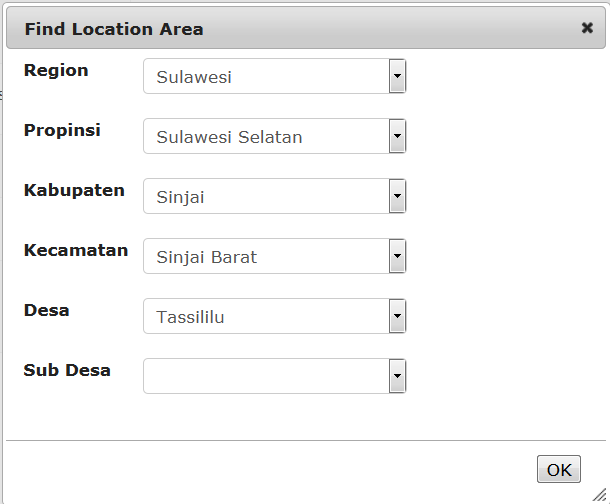
The provincial coordinator for Sulawesi Seletan would be assigned like this
A dinas paravet in Barru, Sulawesi Seletan might be assigned like this
And so on
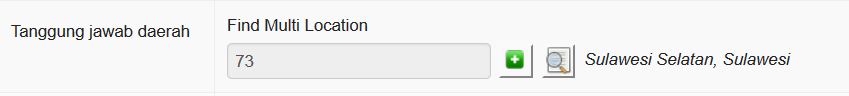
A village reporter (Pelsa) would be assigned as follows
A pelsa with two desa under her responsibility might look something like this
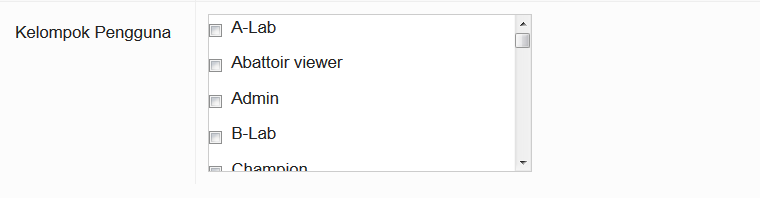
Group
Each user is given a User type and is part of a User Group. Some users are assigned to more than one group. This determines what the person is permitted to do, what data they are permitted to submit and view, and what functions they may perform on the iSIKHNAS website.
Users can be assigned to several user types depending on their roles.
English
| Code | User Type |
|---|---|
| 1 | Champion |
| 2 | Regional coordinator |
| 3 | Provincial coordinator |
| 4 | District coordinator |
| 5 | Vet Services Vet |
| 6 | Vet services paravet |
| 7 | Vet service other staff |
| 8 | Contract Worker |
| 9 | Village reporter |
| 10 | Farmer |
| 11 | Abattoir reporter |
| 12 | Meat inspector |
| 13 | Drug inspector |
| 14 | Check point officer |
| 15 | Quarantine |
| 16 | Public health |
| 17 | A-Lab (DIC) |
| 18 | B-Lab (provincial) |
| 19 | Inseminator |
| 20 | Trainer/demonstrator |
| 21 | Vet services viewer |
| 22 | Quarantine viewer |
| 23 | Public health viewer |
| 24 | Abattoir viewer |
| 25 | Administrator |
| 26 | Provincial Kesmavet Coordinator |
| 27 | National Production Coordinator |
| 28 | Production Provincial Coordinator |
| 29 | Reporting Farmer |
| 30 | Epi Viewer |
| 31 | Project Viewer |
| 32 | Semen collection centre officer |
| 33 | District Production Coordinator |
| 34 | Public Vet |
| 35 | Kader Vaksinator |
| 36 | Head of district livestock and animal health office division |
| 37 | Head of provincial animal health division |
| 38 | Head of dinas vaccination team |
| 39 | data encoder |
| 40 | Head of field vaccination team |
| 68 | C lab |
| 69 | SMS Admin |
| 70 | Survei team |
| 71 | Pregnancy Test Officer |
| 72 | Manager SPR |
| 73 | Tim Upsus Siwab |
| 74 | Superuser |
| 75 | Update locations Officer |
| 76 | Recorder Siwab |
| 77 | champion 1 |
| 78 | champion 2 |
| 79 | Technical Reproduction Assistant |
| 80 | AMPM reporter |
| 81 | Wastukan |
| 82 | Vet Author |
| 83 | Vet Authority Province Level |
| 84 | Sensus Reporting |
| 85 | Logistik Admin |
| 86 | Qurban Inspector |
| 87 | animal traders |
| 88 | API user |
| 89 | Academics |
| 90 | Pelapor Cold Storage |
| 91 | Head of Provincial Services |
| 92 | Head of District Services |
| 93 | Head of Animal Health/Public Veterinary Section |
| 94 | Director of Animal Health |
| 95 | Director of Veterinary Public Health |
| 96 | Kepala Seksi Keswan/Kesmavet Provinsi |
| 97 | Private Abbatoir reporter |
| 98 | Chief Veterinary Officer |
| 99 | Vet Authority Animal Health |
| 100 | Vet Authority Veterunary Public Health |
| 101 | Vet Authority Animal Quarantine |
| 102 | Vet Authority District Level |
| 103 | Head of Technical Unit |
| 104 | Babinsa & Babinkamtibmas |
| 105 | Babinsa atau Babinkamtibmas |
| 106 | Breeding officer |
| 107 | veterinary center staff |
| 108 | Public Reporter |
| 109 | Compartement Reporter |
| 110 | Vets Compartment |
| 111 | Compartement Champion |
Setting permissions
Users are assigned to one or more User Groups.
Each user group has a predefined (default) list of permissions (actions they are allowed to do within the system) and these are managed via the Administration : User Group Permissions.
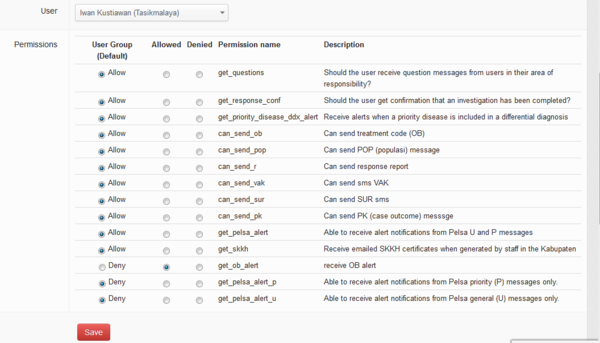
Some permissions can be set differently according to the individual person. This is usually decided by the district coordinator who takes into account the skills and knowledge of each member of staff. The user should be told what he or she may or may not do within the system and why these restrictions are necessary.
Example
Para-vets are usually required to make differential diagnoses - their best guess at what is causing a particular problem in a reported case. The default permission for para-vets is that they CAN diagnose but some coordinators may not want this permission to go to every para-vet on staff. Some para-vets may not have received sufficient training to allow them to make a differential diagnosis confidently. Most para-vets are required to add a differential diagnosis to their U or P field reports of disease. A coordinator may wish to exclude a para-vet with low skills from this step. By setting the permissions differently for this para-vet he will still be able to send U and P reports but these will no longer require him to include a differential diagnosis - it will be more like a pelsa version of the message.
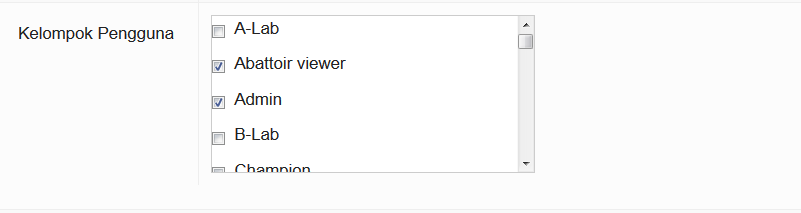
Some field para-vets who report disease may also be abattoir reporters. In this case, they are assigned as two user groups.
Administration: Permissions
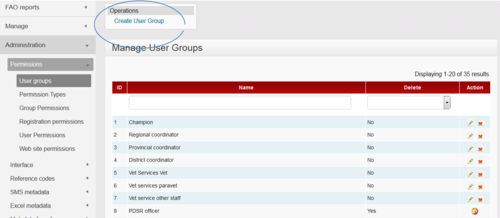
User groups
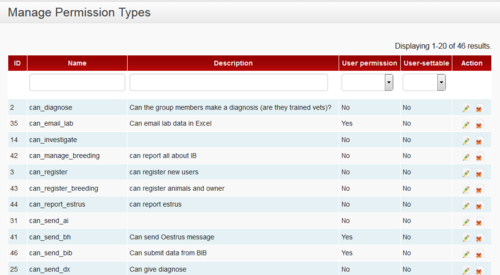
Permission types
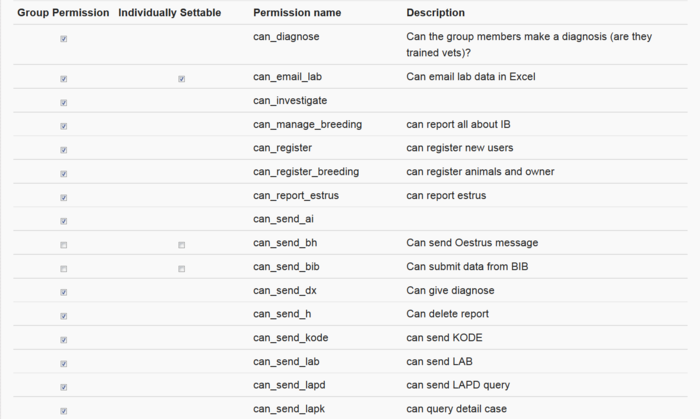
Group permissions
Group permissions are set by Champions only. The permissions reflect the overall policy decisions regulating the use of the system. This is primarily done for security and data integrity reasons to ensure the system stays strong.
Every user group has group default permissions (which are applicable to the entire group) and a few of these are able to be set differently for the individual. This allows the system to respond to the differences between individual staff members and the way each kabupaten wants to manage them. Let's look at an example:
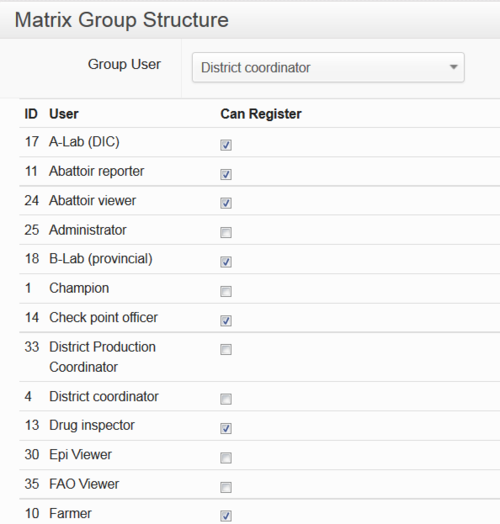
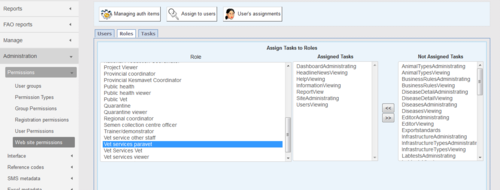
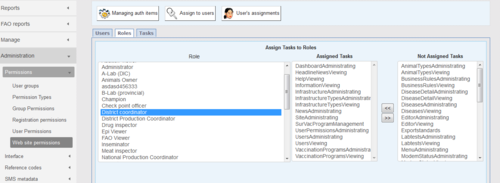
Registration permissions (matrix group structure)
Only certain users of iSIKHNAS are able to register new users. This is to ensure the system remains as secure as possible. Champions are the only ones with permission to change these settings. This example shows part of the list of user types which district coordinators are allowed to register.
Individual user permissions
A coordinator may adjust the user rights for individuals. This function allows the system to respond to the variety which exists between staff. Some staff are more experienced than others, some have more training, others are less capable and are awaiting further training. Here is an example of the flexibility a district coordinator has when managing iSIKHNAS user permissions.
Website permissions
Area of responsibility
- Roles
- Locations
- Personalising the website for users
Analysis of data
- How to ask for a new report to be made
- Defining your question
- Making sense of the outputs
- Printing reports, editing Excel files
- Using the data to support your monitoring role
- Management and support structures
- Roles and responsibilities of everyone involved
- Policy changes, technical issues and assistance with analysis
- Where to go for help
- Role and responsibilities of the coordinator
- How to motivate and reassure staff
- Monitoring the system
- Reacting to problems
- Dealing with questions, requests, problems, flaws
- Giving and sharing feedback
- Developing a culture of ongoing training
- Developing a strong network of village level reporters
- Signs recognition training
- Developing respect for their role and a sense of pride the work they do
- Keeping people involved
Â
Reports
· New
· Disease
· Vaccination
· Surveillance Program
· Movement
· Abattoir
· Laboratory
· Users
· Codes
· System
· View reports
· Saved reports
Manage
· My profile
· Manage users
o User details
o User settings
· Vaccination Programs
· Surveillance Programs
· Infrastructure
· Laboratory tests
· Export lab standards
Administration
Permissions
· user groups,
· user permission types,
· user group permissions,
· registration permissions (matrix group structure),
· individual user permissions,
· website permissions
Interface
· Menu system
· Menu system by Group User
· Generate Interface
· News stories
Reference codes
· Diseases
· Species
· Signs
· Animal types
· Syndromes
· Laboratory
o Testype
o Laboratory sections
o Submission reasons
o Submitter types
o Specimen forms
o Age units
o Test methods
o Test targets
o Qualitative findings
o Units for quantitative findings
o Uncertainty types
o Test results
· Drugs
o Drug class
o Drug types
o Drugs
· Production
o Straws
o Colour
o Animal purposes
o Event types
· Infrastructure types
SMS metadata
· Modem status
· Edit SMS messages
· Edit SMS Fields
· Test SMS message
· Create SMS handler
Excel metadata
· Import jobs
· Import tables
· Import fields
· Field types
Metadata for reference export
·
Business Rules
·
Reports
· Reports
· Saved reports
· Report subscriptions
· Field types
· Regenerate reports for PL/R
Templates
· HTML templates
Roles and responsibilities
Regional and Provincial coordinators
Leadership
- Act as an ambassador, information source and spokesperson for the system at the provincial/regional level
- Safeguard the philosophy and principals upon which iSIKHNAS has been built
- Report both achievements and problems to the Regional Coordinator or Champions
- Respond to requests for assistance, advice or new data reports in a timely and constructive manner.
- Maintain close contact with district coordinators in a supportive and encouraging manner
- Assist district coordinators with their monitoring, support and analysis roles wherever possible.
- Respond to problems common to several district coordinators in a collaborative manner in order to resolve difficulties
- Annual meeting to discuss provincial approaches and issues, share lessons learned and improve monitoring and response.
Support and monitoring
- Monitor the message log and respond quickly to problems in a supportive manner
- Respond to feedback and questions from users in a timely and supportive manner
- Support and improve the pelsa network
- Monitor and evaluate the performance of the team, set goals and priorities for improvement and development
- Identify training needs of staff based on monitoring of field reports
User development and administration
- Assist in the training of district staff and new users
- Ensure kabupaten coordinators are replaced efficiently whenever this becomes necessary
- Ensure user details are up to date
- Facilitate or assist training of specific user groups such as abattoir, production, police or health department, for example.
- Supervise and monitor all registered users in the area of responsibility
- Register local infrastructure and create new location codes where necessary and ensure these are up to date.
Reporting
- Report technical problems, inadequacies or redundancies immediately to the Champions and Regional coordinator
Analysis and management
- Assist in the analysis of data for the evaluation of activities, performance and priority setting.
- Assist in the analysis of data for the purposes of budget advocacy for support for ongoing and new activities
- Make recommendations from the results of data analysis
- Encourage and facilitate surveillance, vaccination and population data collection activities through iSIKHNAS.
District coordinators
Leadership
- Act as an ambassador, information source and spokesperson for the system in the district
- Safeguard the philosophy and principals upon which iSIKHNAS has been built
- Ensure users can access and refer to you easily and freely.
- Share the coordination role with one or more deputies.
- Respond to requests for new data reports or suggested changes
User development and administration
- Register new Pelsa and Dinas users correctly
- Recruit and train new Pelsa and Dinas users in all relevant aspects of the system
- Ensure user details are up to date
- Facilitate or assist training of specific user groups such as abattoir, production, police or health department, for example.
- Supervise and monitor all registered users in the area of responsibility
Support and monitoring
- Monitor the message log and respond quickly to problems in a supportive manner
- Respond to feedback and questions from users in a timely and supportive manner
- Assist para-vets to respect and support the work of village pelsa
- Monitor and evaluate the performance of the team, set goals and priorities for improvement and development
- Identify training needs of staff based on monitoring of field reports
Reporting
- Report technical problems, inadequacies or redundancies immediately to the Champions and Provincial coordinator
Analysis and management
- Assist in the analysis of data for the evaluation of activities, performance and priority setting.
- Assist in the analysis of data for the purposes of budget advocacy for support for ongoing and new activities
- Make recommendations from the results of data analysis
- Manage surveillance, vaccination and population data collection activities through iSIKHNAS.
- Register local infrastructure.
- Manage and update location codes within your area.